On different operation system, have different method to read/write I/O port. I
know WinIO on windows, IoWrite8/16/32 on Linux.
There is a good open source software “Open Hardware Monitor”, which develop by
C# language. It support almost all the motherboard.
- Datasheet of chipsLook the access channels on file NCT6776F_NCT6776D_Datasheet_V1_2
page 275
19.2 ACCESS CHANNELS
There are two different channels to set up/access the GPIO ports. The first one is the indirect access via register
2E/2F (4E/4F, it depends by HEFRAS trapping). The registers can be read / written only when the respective
logical device ID and port number are selected.
known that rigister index is 0x2E, and data Input/Output port is 0x2F
On page 54
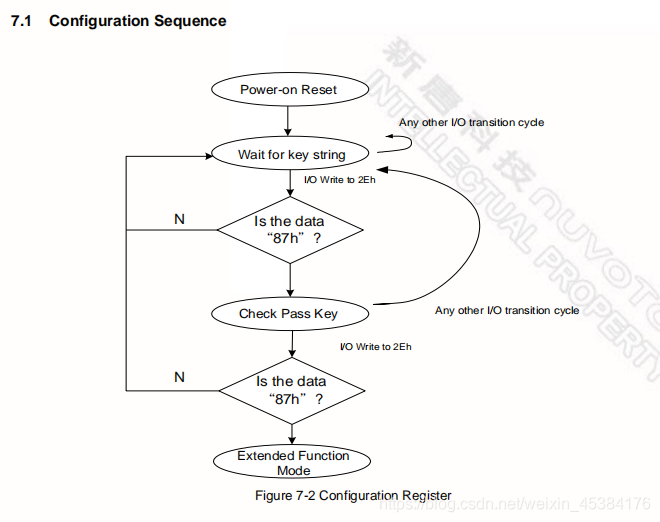
To program the NCT6776F / NCT6776D configuration registers, the following configuration procedures must be
followed in sequence:
(1). Enter the Extended Function Mode.
(2). Configure the configuration registers.
(3). Exit the Extended Function Mode.
7.1.1 Enter the Extended Function Mode
To place the chip into the Extended Function Mode, two successive writes of 0x87 must be applied to Extended
Function Enable Registers (EFERs, i.e. 2Eh or 4Eh).
7.1.2 Configure the Configuration Registers
The chip selects the Logical Device and activates the desired Logical Devices through Extended Function Index
Register (EFIR) and Extended Function Data Register (EFDR). The EFIR is located at the same address as the
EFER, and the EFDR is located at address (EFIR+1).
First, write the Logical Device Number (i.e. 0x07) to the EFIR and then write the number of the desired Logical
Device to the EFDR. If accessing the Chip (Global) Control Registers, this step is not required.
Secondly, write the address of the desired configuration register within the Logical Device to the EFIR and then
write (or read) the desired configuration register through the EFDR.
7.1.3 Exit the Extended Function Mode
To exit the Extended Function Mode, writing 0xAA to the EFER is required. Once the chip exits the Extended
Function Mode, it is in the normal running mode and is ready to enter the configuration mode.
Software Programming Example
The following example is written in Intel 8086 assembly language. It assumes that the EFER is located at 2Eh, so
the EFIR is located at 2Eh and the EFDR is located at 2Fh. If the HEFRAS (CR[26h] bit 6 showing the value of
the strap pin at power on) is set, 2Eh can be directly replaced by 4Eh and 2Fh replaced by 4Fh.
This example programs the configuration register F0h (clock source) of logical device 1 (UART A) to the value of
3Ch (24MHz). First, one must enter the Extended Function Mode, then setting the Logical Device Number (Index
07h) to 01h. Then program index F0h to 3Ch. Finally, exit the Extended Function Mode.
;-----------------------------------------------------
; Enter the Extended Function Mode
;-----------------------------------------------------
MOV DX, 2EH
MOV AL, 87H
OUT DX, AL
OUT DX, AL
;-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
; Configure Logical Device 1, Configuration Register CRF0
;-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOV DX, 2EH
MOV AL, 07H
OUT DX, AL
; point to Logical Device Number Reg.
MOV DX, 2FH
MOV AL, 01H
OUT DX, AL
; select Logical Device 1
;
MOV DX, 2EH
MOV AL, F0H
OUT DX, AL
; select CRF0
MOV DX, 2FH
MOV AL, 3CH
OUT DX, AL
; update CRF0 with value 3CH
;-----------------------------------------------
; Exit the Extended Function Mode
;----------------------------------------------
MOV DX, 2EH
MOV AL, AAH
OUT DX, AL
- Open Hardware MonitorHomepage
- code
The Open Hardware Monitor is a free open source software that monitors
temperature sensors, fan speeds, voltages, load and clock speeds of a computer.
As below, introduct how to use VC++ to monitor HW status on windows:
1). modify computer.cs,add some interface like GetFanSpeed(). if have problem , look report function .
2). set the project properity to output class library.
3). Reference VC++ use C# DLL
1.1 Analyze open-hardware-monitorUse Winbond W83627DHG-P chip as example.
A description about how to monitor hardware, see this
http://www.supermicro.com/support/faqs/faq.cfm?faq=12015
Question
I'm trying to access the Winbond 83627DHG-P IO chip on the motherboard X8SIL.
We want to use the LMsensor. Do you have the offset codes for the smbus?
Answer
Bus Type = ISAIO/SMBus
One W83627DHG-P
Windbond W83627DHG-P, Slave Address=0x2d (0x5a in 8-Bit format)
OR IndexReg=A15, DataReg=A16
Fan1 Fan Speed, Bank 0, Offset 0x29 RPM = 1350000/8/Data
Fan2 Fan Speed, Bank 5, Offset 0x53 RPM = 1350000/8/Data
Fan3 Fan Speed, Bank 0, Offset 0x28 RPM = 1350000/8/Data
Fan4 Fan Speed, Bank 0, Offset 0x3f RPM = 1350000/8/Data
Fan5 Fan Speed, Bank 0, Offset 0x2a RPM = 1350000/8/Data
CPU Voltage, Bank 0, Offset 0x20 Voltage = Data* 0.008
-12V Voltage, Bank 0, Offset 0x26 Voltage = ((Data*0.008-2.048)/(10./242.))+2.048
+12V Voltage, Bank 0, Offset 0x21 Voltage = Data* 0.008/ (10./66.2)
AVCC Voltage, Bank 0, Offset 0x22 Voltage = Data* 0.016
3.3Vcc Voltage, Bank 0, Offset 0x23 Voltage = Data* 0.016
DIMM Voltage, Bank 0, Offset 0x24 Voltage = Data* 0.008
+5V Voltage, Bank 0, Offset 0x25 Voltage = Data* 0.008/ (10./40.)
+3.3VSb Voltage, Bank 5, Offset 0x50 Voltage = Data* 0.016
VBAT Voltage, Bank 5, Offset 0x51 Voltage = Data* 0.016
CPU Temperature, Bank 1, Offset 0x50 Temperature = Data
System Temperature, Bank 2, Offset 0x50 Temperature = Data
Chassis Intrusion, Bank 0, Offset 0x42, BitMask 0x10 1 = Bad, 0 = Good
(Clear Bit: Bank 0, Offset 0x46, BitMask 0x80)
Power Supply Failure, GP23(From W83627DHG-P) 1 = Good, 0 = Bad
1.1.1 File: Hardware/LPC/LPCIO.csIO Ports
// I/O Ports
private readonly ushort[] REGISTER_PORTS = new ushort[] { 0x2E, 0x4E };
private readonly ushort[] VALUE_PORTS = new ushort[] { 0x2F, 0x4F };
Winbond, Nuvoton, Fintek
private const byte FINTEK_VENDOR_ID_REGISTER = 0x23;
private const ushort FINTEK_VENDOR_ID = 0x1934;
private const byte WINBOND_NUVOTON_HARDWARE_MONITOR_LDN = 0x0B;
private const byte F71858_HARDWARE_MONITOR_LDN = 0x02;
private const byte FINTEK_HARDWARE_MONITOR_LDN = 0x04;
private void WinbondNuvotonFintekEnter() {
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, 0x87);
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, 0x87);
}
private void WinbondNuvotonFintekExit() {
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, 0xAA);
}
ITE
private const byte IT87_ENVIRONMENT_CONTROLLER_LDN = 0x04;
private const byte IT8705_GPIO_LDN = 0x05;
private const byte IT87XX_GPIO_LDN = 0x07;
private const byte IT87_CHIP_VERSION_REGISTER = 0x22;
private void IT87Enter() {
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, 0x87);
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, 0x01);
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, 0x55);
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, 0x55);
}
private void IT87Exit() {
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, CONFIGURATION_CONTROL_REGISTER);
Ring0.WriteIoPort(valuePort, 0x02);
}
SMSC
private void SMSCEnter() {
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, 0x55);
}
private void SMSCExit() {
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, 0xAA);
}
How to get value:call ReadByte to get value:
byte id = ReadByte(CHIP_ID_REGISTER);
byte revision = ReadByte(CHIP_REVISION_REGISTER);
look at function ReadByte:
private byte ReadByte(byte register) {
Ring0.WriteIoPort(registerPort, register);
return Ring0.ReadIoPort(valuePort);
}
first, write register value to registerPort;
second, read value from valueport.
1.1.2 File: Hardware/LPC/W836XX.csHow to get value:// Hardware Monitor
private const byte ADDRESS_REGISTER_OFFSET = 0x05;
private const byte DATA_REGISTER_OFFSET = 0x06;
// Hardware Monitor Registers
private const byte BANK_SELECT_REGISTER = 0x4E;
private byte ReadByte(byte bank, byte register) {
Ring0.WriteIoPort(
(ushort)(address + ADDRESS_REGISTER_OFFSET), BANK_SELECT_REGISTER);
Ring0.WriteIoPort(
(ushort)(address + DATA_REGISTER_OFFSET), bank);
Ring0.WriteIoPort(
(ushort)(address + ADDRESS_REGISTER_OFFSET), register);
return Ring0.ReadIoPort(
(ushort)(address + DATA_REGISTER_OFFSET));
}
What is the value of “address”:set value by construction
public W836XX(Chip chip, byte revision, ushort address) {
this.address = address;
this.revision = revision;
this.chip = chip;
...
}
on LPCIO.cs, found the calling code:
private const byte BASE_ADDRESS_REGISTER = 0x60;
ushort address = ReadWord(BASE_ADDRESS_REGISTER);
switch (chip) {
case Chip.W83627DHG:
case Chip.W83627DHGP:
case Chip.W83627EHF:
case Chip.W83627HF:
case Chip.W83627THF:
case Chip.W83667HG:
case Chip.W83667HGB:
case Chip.W83687THF:
superIOs.Add(new W836XX(chip, revision, address));
break;
...
}
Get temperature:private readonly byte[] TEMPERATURE_REG = new byte[] { 0x50, 0x50, 0x27 };
private readonly byte[] TEMPERATURE_BANK = new byte[] { 1, 2, 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < temperatures.Length; i++) {
int value = ((sbyte)ReadByte(TEMPERATURE_BANK[i],
TEMPERATURE_REG[i])) 0)
value |= ReadByte(TEMPERATURE_BANK[i],
(byte)(TEMPERATURE_REG[i] + 1)) >> 7;
float temperature = value / 2.0f;
if (temperature = -55 && !peciTemperature[i]) {
temperatures[i] = temperature;
} else {
temperatures[i] = null;
}
}
Get fan speed:call ReadByte(FAN_TACHO_BANK[i], FAN_TACHO_REG[i]) to get speed value to “count”
, then set real fan spee to array variable “fans[]“.
private readonly byte[] FAN_TACHO_REG =
new byte[] { 0x28, 0x29, 0x2A, 0x3F, 0x53 };
private readonly byte[] FAN_TACHO_BANK =
new byte[] { 0, 0, 0, 0, 5 };
private readonly byte[] FAN_BIT_REG =
new byte[] { 0x47, 0x4B, 0x4C, 0x59, 0x5D };
private readonly byte[] FAN_DIV_BIT0 = new byte[] { 36, 38, 30, 8, 10 };
private readonly byte[] FAN_DIV_BIT1 = new byte[] { 37, 39, 31, 9, 11 };
private readonly byte[] FAN_DIV_BIT2 = new byte[] { 5, 6, 7, 23, 15 };
ulong bits = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < FAN_BIT_REG.Length; i++)
bits = (bits > FAN_DIV_BIT2[i]) & 1) > FAN_DIV_BIT1[i]) & 1) > FAN_DIV_BIT0[i]) & 1));
int divisor = 1 192 && divisorBits < 7)
divisorBits++;
if (count < 96 && divisorBits > 0)
divisorBits--;
newBits = SetBit(newBits, FAN_DIV_BIT2[i], (divisorBits >> 2) & 1);
newBits = SetBit(newBits, FAN_DIV_BIT1[i], (divisorBits >> 1) & 1);
newBits = SetBit(newBits, FAN_DIV_BIT0[i], divisorBits & 1);
}
Referenced from:https://matrix207.github.io/2012/12/17/monitor-hardware-status/